INJECTION MOULDING
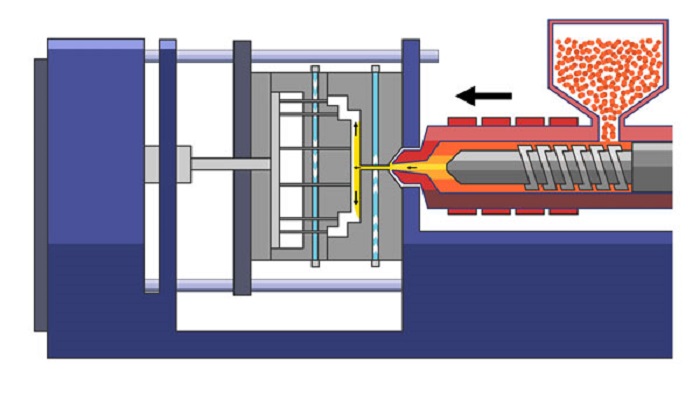 Injection molding is the most commonly used manufacturing process for the fabrication of plastic parts. A wide variety of products are manufactured using injection molding, which varies greatly in size, complexity, and application. The injection molding process requires the use of an injection molding machine, raw plastic material, and a mold. The plastic is melted in the injection molding machine and then injected into the mold, where it cools and solidifies into the final part. The steps in this process are described in greater detail in the next section. Injection molding is used to produce thin-walled plastic parts for a wide variety of applications, one of the most common being plastic housings.
Injection molding is the most commonly used manufacturing process for the fabrication of plastic parts. A wide variety of products are manufactured using injection molding, which varies greatly in size, complexity, and application. The injection molding process requires the use of an injection molding machine, raw plastic material, and a mold. The plastic is melted in the injection molding machine and then injected into the mold, where it cools and solidifies into the final part. The steps in this process are described in greater detail in the next section. Injection molding is used to produce thin-walled plastic parts for a wide variety of applications, one of the most common being plastic housings.
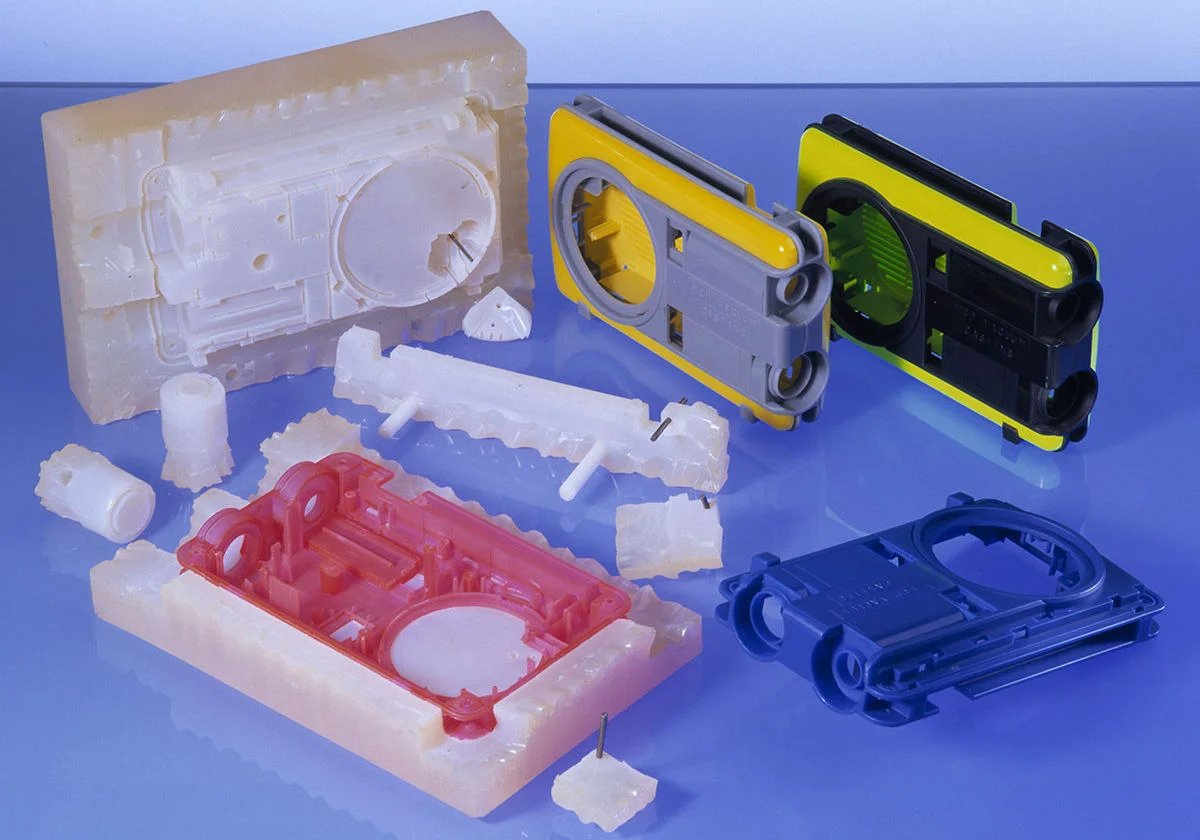
The plastic housing is a thin-walled enclosure, often requiring many ribs and bosses on the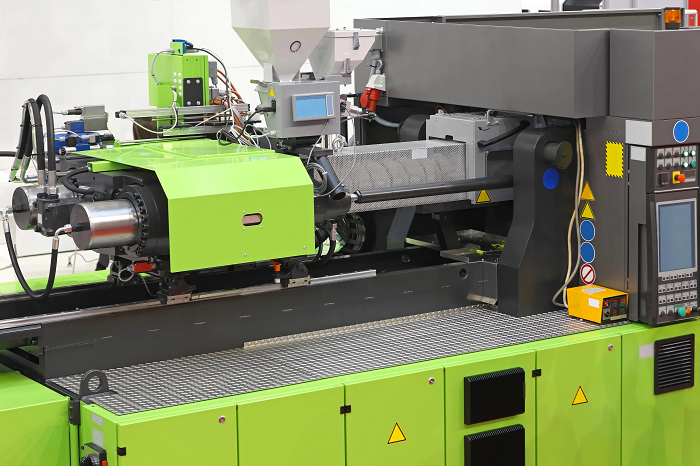 interior. These housings are used in a variety of products including household appliances, consumer electronics, power tools, and as automotive dashboards. Other common thin-walled products include different types of open containers, such as buckets. Injection molding is also used to produce several everyday items such as toothbrushes or small plastic toys. Many medical devices, including valves and syringes, are manufactured using injection molding as well.
interior. These housings are used in a variety of products including household appliances, consumer electronics, power tools, and as automotive dashboards. Other common thin-walled products include different types of open containers, such as buckets. Injection molding is also used to produce several everyday items such as toothbrushes or small plastic toys. Many medical devices, including valves and syringes, are manufactured using injection molding as well.
VACUUM CASTING
 Vacuum casting (VC) is a manufacturing technology that uses a vacuum to draw liquid casting material into a mold. It differs significantly from injection molding, which pushes liquid material into a mold using a screw. The process starts with a master model, which a 3D Model creates using one of its 3D Printing machinings. This master model is then immersed in liquid silicone, which is cured and becomes the mold.
Vacuum casting (VC) is a manufacturing technology that uses a vacuum to draw liquid casting material into a mold. It differs significantly from injection molding, which pushes liquid material into a mold using a screw. The process starts with a master model, which a 3D Model creates using one of its 3D Printing machinings. This master model is then immersed in liquid silicone, which is cured and becomes the mold.
 Once it has been cut and the master model removed, the silicone mold can be put to use. This stage involves pouring casting resin into the mold, as the vacuum removes bubbles and air pockets to ensure a smooth finish. The resin part is then cured in an oven and removed from the silicone mold after cooling down, which can be reused around 20 times. Each cast part is an exact copy of the original master model. It’s a perfect solution for rapid prototyping and making small batches of quality parts.
Once it has been cut and the master model removed, the silicone mold can be put to use. This stage involves pouring casting resin into the mold, as the vacuum removes bubbles and air pockets to ensure a smooth finish. The resin part is then cured in an oven and removed from the silicone mold after cooling down, which can be reused around 20 times. Each cast part is an exact copy of the original master model. It’s a perfect solution for rapid prototyping and making small batches of quality parts.
Courtesy: NextGen3DTech









